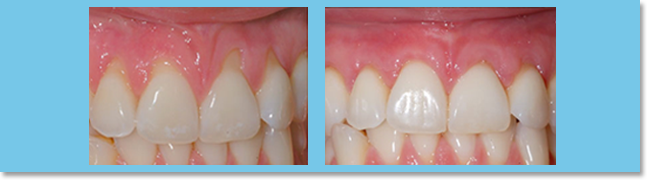
Periodontics
Periodontal diseases affect the supporting areas of the teeth, which can be divided into two main divisions: gingivitis and periodontitis. Periodontitis is the main cause of tooth loss in adults. It is also found that there is a close correlation between periodontal health and major body diseases, such as stroke and circulatory illnesses.
Indications of periodontal disease are: gum bleeding, gum recession, erythema and edema, loose tooth, and toothache under pressure.
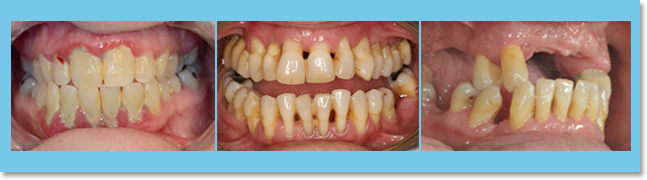

Factors related to Periodontal Diseases
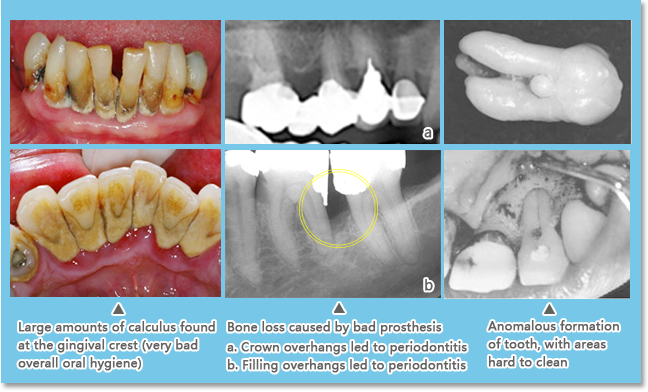
The major contributing factors are plaque and calculus. Therefore, bad oral hygiene, smoking and prosthesis with overhands are the most common reasons, but genetic make-up, stress, diabetes and anomalous formation of teeth also play a part in the chances of periodontal disease:

Periodontal Treatment Methods
1. Nonsurgical Treatment of the Periodontium
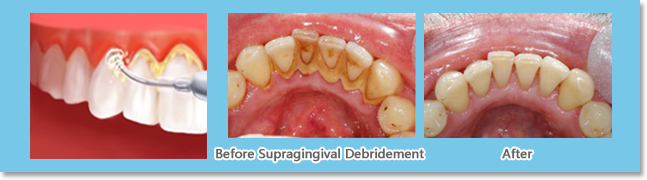
a. Supragingival Debridement (Teeth cleaning)
With the involvement of ultrasonic tips, this treatment aims to remove supragingival plaque, calculus, and stain through tooth-crown scaling. Superior equipment and technique guarantee both a thorough cleaning and comfortable experience.
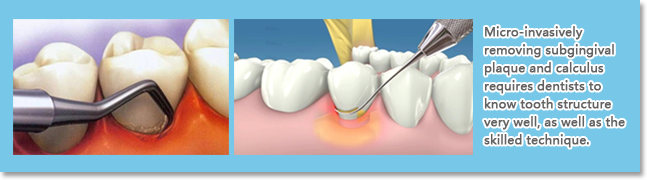
b. Subgingival Debridement
Subgingival Debridement is to remove subgingival plaque and calculus through root-surface scaling and root planning. This treatment usually involves hand instrumentation.
2. Periodontal Surgery Techniques
a. Periodontal Flap Surgery
In cases with deep periodontal pockets, a loosened section of tissue is separated from the adjacent tissues to enable elimination of deposits under better viewing.
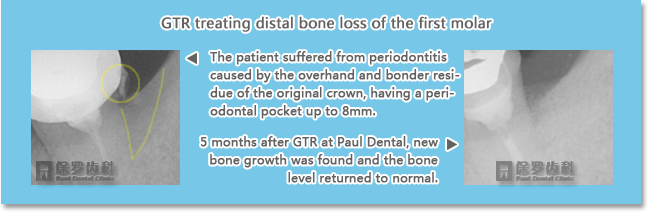
b. Guided Tissue Regeneration
This method can restore and adjust the marginal ridge, encouraging the growth of new periodontal attachment.

c. Gingival Augmentation
Soft tissue grafting helps to restore the gingival crest to a natural height, solving the esthetic problem and sensitivity by covering exposed roots. Ridge augmentation is usually applied in collapsed areas where the implant is placed.